Table of Contents
A lump behind ear can be a worrying sign, as it may indicate the presence of an underlying health condition. These lumps can happen for many reasons and can be a tumor. Depending on the cause, lumps behind the ear may be painful or painless, varying in size and thickness. Other symptoms, such as fever, difficulty swallowing, or difficulty breathing, can sometimes happen. If you find a lump behind ear, it is crucial to have it evaluated by a doctor. It is essential not to ignore a lump behind the ear, as early diagnosis and treatment can often lead to the best outcomes. This article will tell you the causes of the lump behind ear and the treatments to cure it.
Lump Behind Ear: Causes
It is concerning, as it may indicate an underlying health condition. These lumps, also known as masses or nodules, can occur for various reasons and may vary in size, consistency, and level of discomfort. If you have noticed a lump behind your ear, get it evaluated by a healthcare professional, who can determine the cause and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Infections:
Infections that can cause lumps to include abscesses and cellulitis. Abscesses are collections of pus that can develop anywhere on the body, including behind the ear. It happens because of bacteria and can have symptoms such as pain, redness, and fever. Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection and underlying tissue that can cause redness, swelling, and warmth behind the ear. If you dont treat it perfectly, these infections can spread and potentially lead to severe complications.
Inflammation:
Inflammation can also cause a lump behind ear. It is the body’s response to injury or irritation and can cause swelling and redness. Conditions that can cause inflammation behind the ear include allergies, eczema, and dermatitis. They can cause symptoms such as swelling, itching, and redness. Eczema is a skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Dermatitis can cause allergies, irritants, and infections.
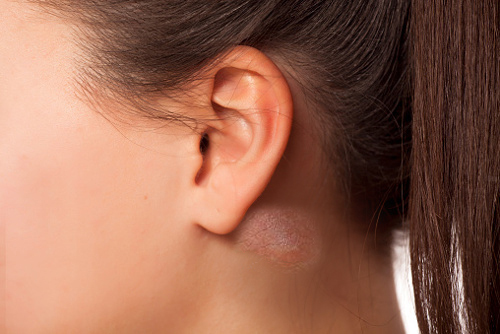
Cysts:
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in various parts of the body and behind the ear. They are usually benign (non-cancerous) and may not cause any harm. It will feel smooth when you touch them. However, if a cyst becomes infected or grows large enough to press on surrounding structures, it can cause discomfort.
Tumors:
Tumors are abnormal growths of cells and can be either benign or malignant (cancerous). Non Cancerous tumors are not cancerous and do not spread to other body parts. They may grow slowly or quickly, and they may or may not cause discomfort. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body. They may overgrow and have other symptoms like weight loss and changes.
Lipoma:
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor of fat cells. They are typically small, soft, and movable. However, if a lipoma grows large enough, it may cause discomfort or interfere with surrounding structures. These are usually harmless, but if you have any new or unusual lumps, go to a doctor who can confirm the diagnosis and suggest proper treatment if required. In some cases, surgical removal of the lipoma is better, especially if it causes discomfort or affects the function of nearby body parts.
Enlarged Lymph Nodes:
Enlarged lymph nodes, also known as swollen lymph nodes, can occur for various reasons, including infection, inflammation, or the presence of a tumor. These small, bean-shaped structures are part of the body’s immune system and help fight infections. Lymph nodes can become enlarged in response to infection, inflammation, or other types of injury. They may be tender to the touch and have symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or swelling in different body parts. In some cases, swollen lymph nodes may indicate an underlying health condition such as cancer.
Mastoiditis:
This infection happens in mastoid bone found behind the ear. The mastoid bone is a spongy bone that contains air spaces and is part of the ear’s temporal bone. Other conditions, such as sinusitis or meningitis, can also cause it. The area behind the ear may become swollen, red, and tender to the touch. It can also cause hearing loss and dizziness. If left untreated, mastoiditis can lead to severe complications, such as meningitis or brain abscess. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and possibly surgery to remove infected tissue.
These are just a few causes of the many potential causes of a lump behind ear. A doctor can determine the specific cause of a lump and do the treatment. Treatment may include medications, surgical removal, or other therapies.

When To See a Doctor?
When you see a lump behind your ear for the first time, you will probably freak out and think you need medication as soon as possible. However, most of the lumps behind the ear are harmless, and you don’t need any medical attention. See a healthcare professional if you have a new or unusual lump behind your ear. Surprisingly, you will need to see a doctor if the lump has a bacterial infection. It can be a sign of another health condition, and you have it evaluated to determine the cause and recommend the appropriate treatment. A healthcare professional can examine the lump and potentially order tests such as an X-ray or biopsy to help determine the cause. Treatment will depend on the cause of the lump but may include medications, surgical removal, or other therapies.
Treatments:
If you find a lump, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can often lead to the best outcomes, so don’t ignore a lump behind ear.
Here are some treatments your doctor may give you; most treatment depends on the condition.
Medications:
If an infection causes the lump, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection. These medications can be taken orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection. Other medications are anti-inflammatory drugs for inflammation or pain relief medications for discomfort. Take these medications as directed and complete the entire course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve. Stopping treatment early can allow the infection to return or may lead to the development of bacteria.
Surgical removal:
The doctor may recommend surgical removal if the lump is a cyst, tumor, or other growth. This involves a simple surgical procedure to remove the lump, or it may be more complex depending on the lump’s size and location. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the type and size of the lump, its location, and other factors that may affect the surgery.
Other therapies:
Radiation therapy or chemotherapy is the treatment of cancerous lumps. These treatments use high-energy waves or chemicals to kill cancer cells, and they may be used alone or in combination with other treatments such as surgery or medications. Physical therapy or occupational therapy to help improve function if the lump is causing mobility or dexterity issues. These therapies may involve exercises or other techniques to help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Always attend follow-up appointments as recommended to monitor the lump and ensure that it resolves or responds to treatment as expected.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, whenever you see a lump behind ear, don’t freak out, it’s not always going to be a cancer tumor. Simply, go to a doctor and tell him your problem. Doctors are professional and they will do a perfect treatment of your condition. After our post, now you know the causes and treatments of lump behind ear. My suggestion would always go to a doctor cause if the lump is cancerous then it is harmful to you. In this type of case, early treatments are better for the patient. Lastly, tell us your experience if you had a lump.









